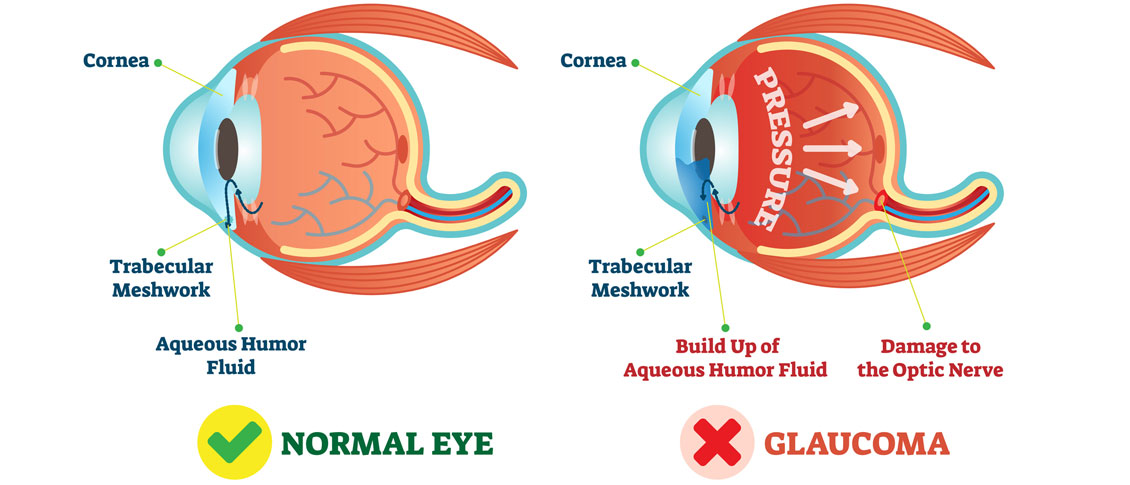
There are several different variations of Glaucoma, but in this article we will mainly focus on Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. This means that there is no specific underlying cause for the Glaucoma like inflammation, trauma or a severe cataract. It also means that the drainage angle where fluid is drained from the inside of the eye into the bloodstream is not narrow or closed.
Closed or Narrow Angle Glaucoma, which will be discussed in another article, is treated differently from Open Angle Glaucoma
In the U.S., Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) is by far the most common type of Glaucoma we treat.
Glaucoma is a disease where the Optic Nerve in the back of the eye deteriorates over time, and that deterioration has a relationship to the Intraocular Pressure (IOP). Most - but not all - people diagnosed with Glaucoma have an elevated IOP. Some people have fairly normal IOP’s but show the characteristic deterioration in the Optic Nerve. Regardless of whether or not the pressure was high initially, our primary treatment is to lower the IOP. We usually are looking to try to get the IOP down by about 25% from the pre-treatment levels.
The two mainstays of initial treatment for POAG in the U.S. are medications or laser treatments. There are other places in the world where Glaucoma is initially treated with surgery. However, while surgery can often lower the pressure to a greater degree than either medications or laser treatments, it comes with a higher rate of complications. Most U.S. eye doctors elect to go with the more conservative approach and utilize either medications - most often in the form of eye drops - or a laser treatment.
Drops
There are several different classes of medications used to treat Glaucoma.
The most common class used are the Prostaglandin Analogues or PGA’s. The PGA’s available in the U.S. are Xalatan (latanaprost), Travatan (travapost), Lumigan (bimatoprost) and Zioptan (tafluprost).
PGA’s are most doctors’ first line of treatment because they generally lower the IOP better than the other classes; they are reasonably well tolerated by most people; and they are dosed just once a day, while most of the other drugs available have to be used multiple times a day.
The other classes of drugs include beta-blockers that are used once or twice a day; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAI’s ), which come in either a drop or pill form and are used either twice or three times a day; alpha agonists that are used either twice or three times a day; and miotics, which are used three or four times a day. All of these other medications are typically used as either second-line or adjunctive treatment when the PGA’s are not successful in keeping the pressure down as single agents.
There are also several combination drops available in the U.S. that combine two of the second-line agents (Cosopt, Combigan, and Symbrinza).
Laser
The second option as initial treatment is a laser procedure.
The two most common laser treatments for Open Angle Glaucoma are Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty (ALT) or Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT). These treatments try and get an area inside the eye called the Trabecular Meshwork - where fluid is drained from the inside of the eye into the venous system - to drain more efficiently.
These treatments tend to lower the pressure to about the same degree as the PGA’s do with over 80% of patients achieving a significant decrease in their eye pressure that lasts at least a year. Both laser treatments can be repeated if the pressure begins to rise again in the future but the SLT works slightly better as a repeat procedure compared to the ALT.
Article contributed by Dr. Brian Wnorowski, M.D.
 Just like adults, children need to have their eyes examined. This need begins at birth and continues through adulthood.Following are common recommendat...
Just like adults, children need to have their eyes examined. This need begins at birth and continues through adulthood.Following are common recommendat...


